Tailor-made for you.
We work closely with our clients to understand their specific requirements and provide the customized product that best fits their needs.
What does the test involve ?
1. Preparation
Some preparation is required before the test. This preparation involves discontinuing certain medications and fasting. Prior to taking the sample, the patient must drink a high-sugar solution.
2. Digestion
If a person has a sugar intolerance, the sugar isn't fully absorbed in the small intestine and passes into the large intestine. There, gut bacteria ferment it, leading to increased production of gases like hydrogen, methane, and sometimes hydrogen sulfide.
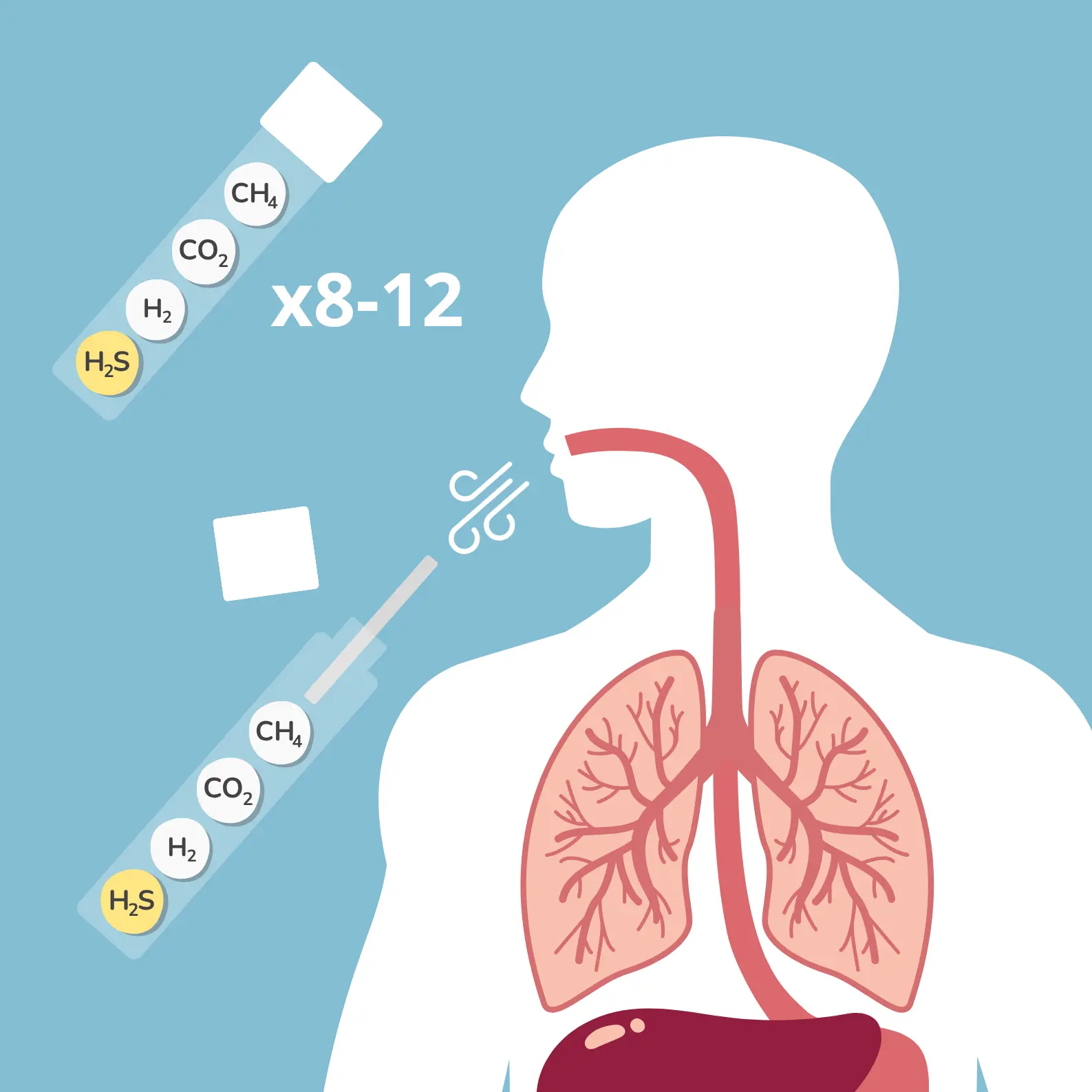
3. Sampling
After drinking the solution, the patient exhales into a tube using a straw to measure gas levels. This process must be repeated at regular intervals over the next three hours to monitor changes in gas production.
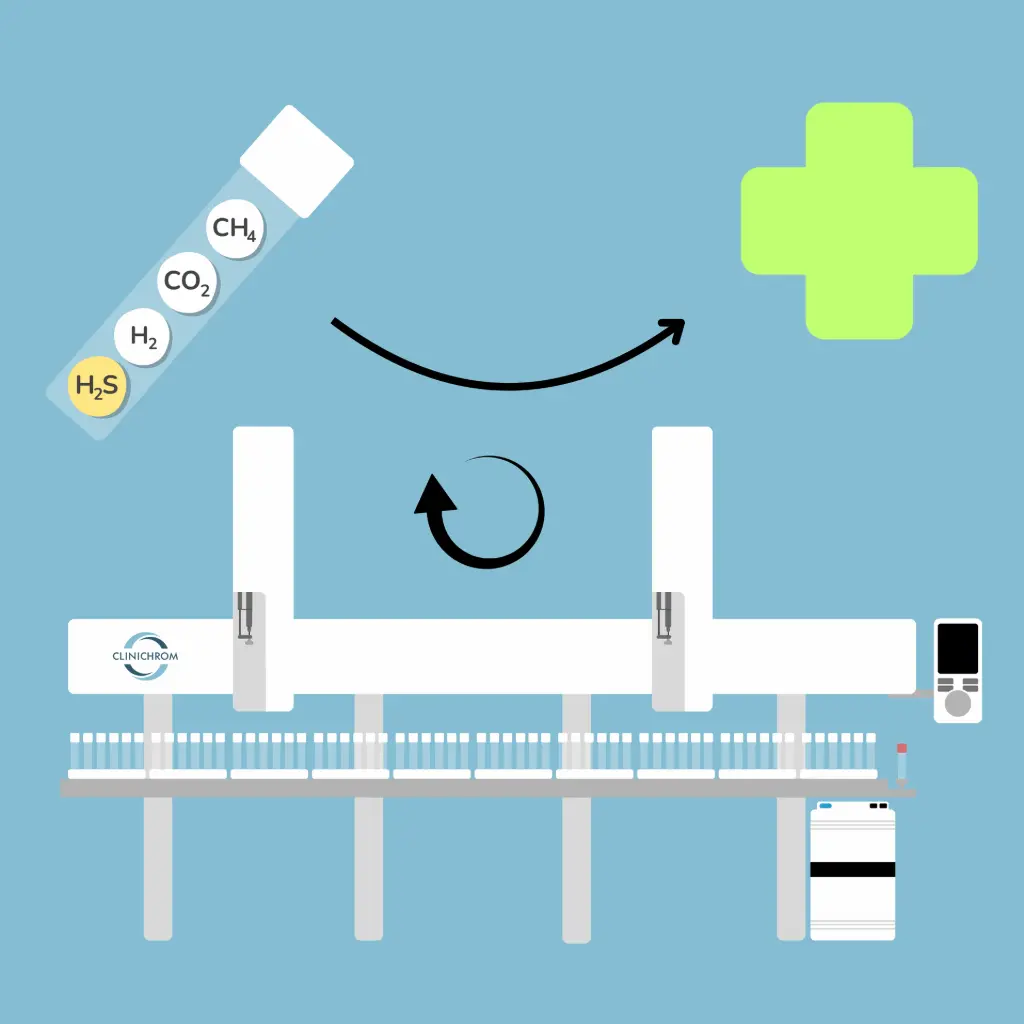
4. Analysis
The lab technician simply reads the 1D/2D barcodes, loads the labeled tubes into the carousel and starts the sequence. The robot injects the sample into the MicroGC, which reports hydrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide levels in under 2 minutes.
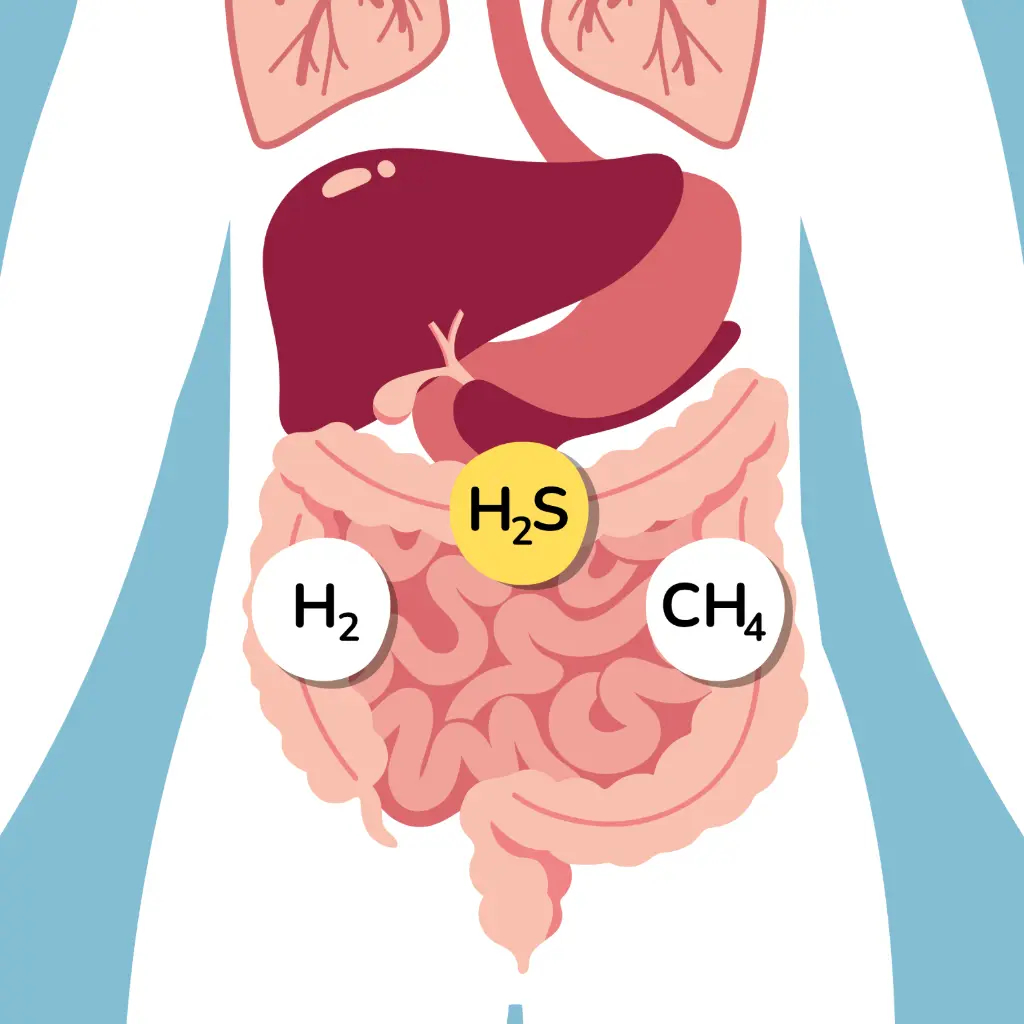
Why does a patient need a breath test ?
This test is carried out to verify if the patient can properly absorb a specific sugar; in some cases, the body cannot digest sugars like lactose or fructose. The test measures a byproduct of sugar breakdown (hydrogen and methane in gas phase) in the breath. If the sugar is not absorbed correctly, gut bacteria ferment it, producing hydrogen, methane and potentially hydrogen sulfide as a byproduct. Under normal circumstances, there is little to no presence of these gases in the breath. This will remain unchanged if the sugar is absorbed in the intestine.